What is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma
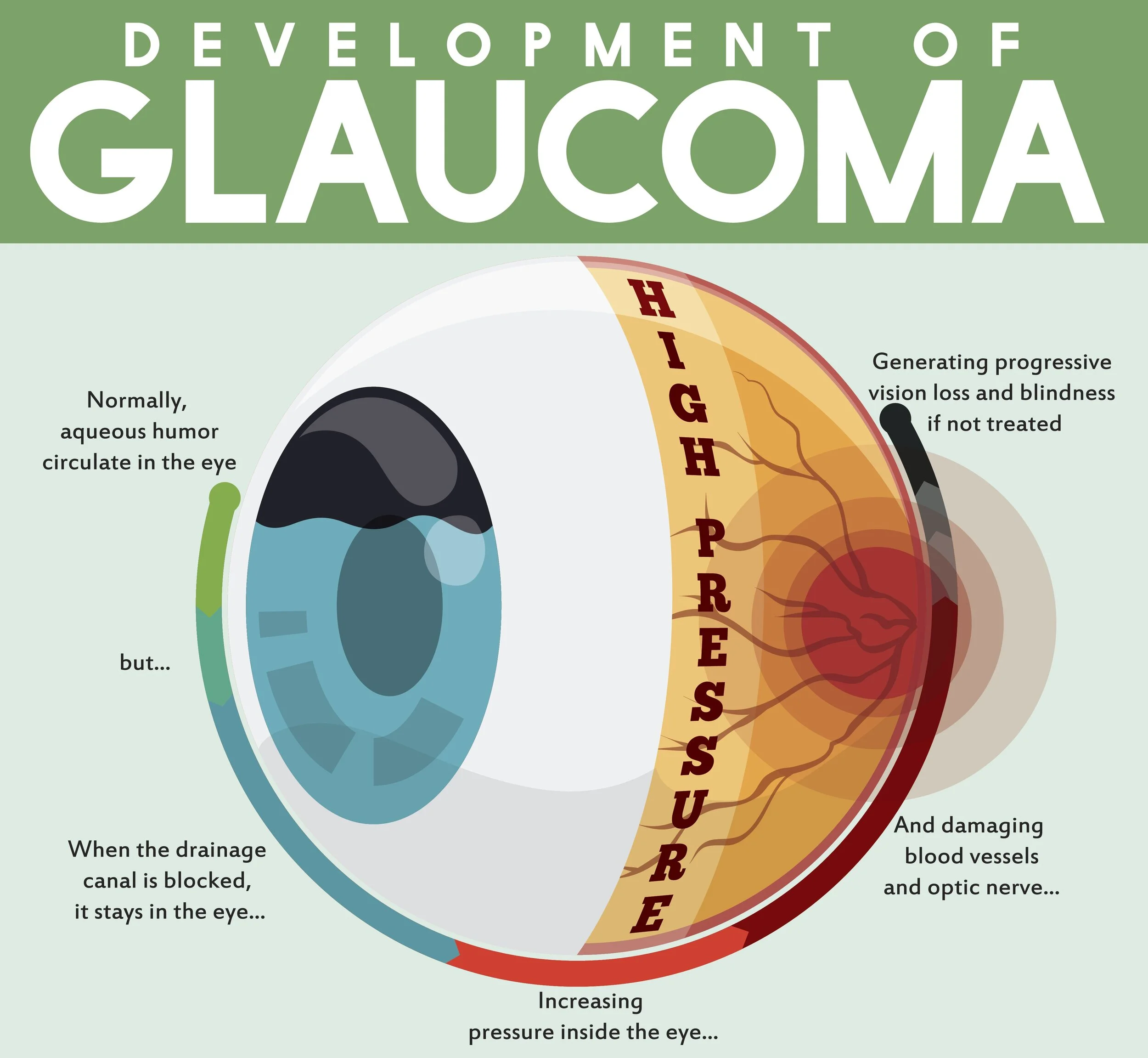
Glaucoma is a group of eye disorders that lead to progressive damage to the optic nerve. The optic nerve is a bundle of about 1 million individual nerve fibers that transmits the visual signals from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma is characterized by loss of nerve tissue that results in vision loss.
The most common form of glaucoma, primary open-angle glaucoma, develops slowly and often without symptoms. Glaucoma is considered the "sneak thief of sight" as it seldom causes pain or other symptoms. Initially, glaucoma affects peripheral or side vision, but it can advance to central vision loss. If left untreated, glaucoma can lead to significant vision loss or even blindness.
In primary open-angle glaucoma, the fluid pressure inside the eye increases. This pressure increase can cause progressive damage to the optic nerve and a loss of nerve fibers. Advanced glaucoma can lead to blindness. Not everyone with high eye pressure will develop glaucoma, and some people with normal eye pressure will develop glaucoma.
A less common type of glaucoma, acute angle-closure glaucoma, usually occurs abruptly due to a rapid increase of pressure in the eye. Its symptoms may include severe eye pain, nausea, redness in the eye, seeing halos or colored rings around lights and blurred vision. This is an emergency condition in which severe vision loss can occur quickly. Glaucoma cannot currently be prevented. But if it is diagnosed and treated early, it can usually be controlled. Medication or surgery can slow or prevent further vision loss. However, vision already lost to glaucoma cannot be restored
Glaucoma is the second-leading cause of blindness in the U.S. It most often occurs in people over age 40, although an infant form of glaucoma exists.
Causes & risk factors
There are many theories about the causes of glaucoma, but the exact cause is unknown. Although the disease is usually associated with an increase in fluid pressure inside the eye, other theories include a lack of adequate blood supply to the nerve.
The following factors can increase the risk of developing glaucoma:
Age. People over age 60 are at increased risk for the disease. African Americans, however, are at increased risk after age 40. The risk of developing glaucoma increases slightly with each year of age.
Race. African Americans are significantly more likely to get glaucoma than Caucasians, and they are much more likely to suffer permanent vision loss. People of Asian descent and Native Alaskans are at higher risk of angle-closure glaucoma. People of Japanese descent are more likely to develop low-tension glaucoma.
Family history of glaucoma. Having a family history of glaucoma increases the risk of developing glaucoma.
Medical conditions. Some studies indicate that diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease may increase the risk of developing glaucoma.
Physical injuries to the eye. Severe trauma, such as being hit in the eye, can result in immediate increased eye pressure. Internal damage from such a trauma can also cause future increases in pressure. Injury can also dislocate the lens, closing the drainage angle and increasing pressure.
Other eye-related risk factors. Certain features of eye anatomy, namely thinner corneas and optic nerve sensitivity, indicate an increased risk for developing glaucoma. Conditions such as retinal detachment, eye tumors, and eye inflammations may also trigger glaucoma. Some studies suggest that high amounts of nearsightedness may also be a risk factor for glaucoma.
Corticosteroid use. Using corticosteroids (including cortisone, hydrocortisone, and prednisone) for prolonged periods of time appears to put some people at risk of developing secondary glaucoma.
Symptoms
The signs or symptoms of glaucoma can vary depending on the type. Primary open-angle glaucoma often develops slowly and painlessly, with no early warning signs. It can gradually destroy one's vision without even knowing it. The first indication that a person has glaucoma may occur after some vision has been lost.
Acute angle-closure glaucoma results from a sudden blockage of drainage channels in the eye, causing a rapid buildup of pressure. In this form of the disease, a patient would have blurred vision, the appearance of halos or colored rings around lights, and pain and redness in the eye.
Diagnosis
Glaucoma is diagnosed through a comprehensive eye examination. Because glaucoma is a progressive disease, meaning it worsens over time, a change in the appearance of the optic nerve, a loss of nerve tissue, and a corresponding loss of vision confirm the diagnosis. Some optic nerves may resemble nerves with glaucoma, but the patients may have no other risk factors or signs of glaucoma. These patients should have routine comprehensive exams to monitor any changes.
Glaucoma testing includes:
Patient history to determine any symptoms the patient is experiencing and if there are any general health problems and family history that may be contributing to the problem.
Visual acuity measurements to determine if vision is being affected.
Tonometry to measure the pressure inside the eye to detect increased risk factors for glaucoma.
Pachymetry to measure corneal thickness. People with thinner corneas are at an increased risk of developing glaucoma.
Visual field testing, also called perimetry, to check if the field of vision has been affected by glaucoma. This test measures your side (peripheral) vision and central vision by either determining the dimmest amount of light that can be detected in various locations of vision, or by determining sensitivity to targets other than light.
Evaluation of the retina of the eye, which may include photographs or scans of the optic nerve, to monitor any changes over time.
Supplemental testing, which may include gonioscopy. This procedure offers a view of the angle anatomy, which is where eye fluid drainage occurs. Serial tonometry is another possible test. This procedure acquires several pressure measurements over time, looking for changes in the eye pressure throughout the day. In addition, devices can be used to measure nerve fiber thickness and to look for tissue loss on specific areas of the nerve fiber layer.
Treatment
Glaucoma treatment is aimed at reducing pressure in the eye. Regular use of prescription eye drops are the most common and often the first treatment. Some cases may require systemic medications, laser treatment, or other surgery. While there is not yet a cure for glaucoma, early diagnosis and continuing treatment can preserve eyesight.
Medications
A number of medications are currently available to treat glaucoma. Typically, medications reduce elevated pressure in the eye. The type of medication may change if it is not reducing pressure enough or if the patient is experiencing side effects.
Surgery
Procedures include laser treatment, making a drainage flap in the eye, inserting a drainage valve, or destroying the tissue that creates the fluid in the eye. All procedures aim to reduce the pressure inside the eye when medication is not sufficient. Surgery cannot reverse vision loss.
Treatment for acute angle-closure glaucoma
Acute angle-closure glaucoma is a medical emergency. Those affected can take medication to reduce eye pressure as quickly as possible. They will also likely undergo a laser procedure called laser peripheral iridotomy. In this procedure, a laser beam creates a small hole in the iris to allow fluid to flow more freely into the front chamber of the eye, where it then can drain.
Prevention
There is no cure for glaucoma. Patients with glaucoma need to continue treatment for the rest of their lives. Because the disease can progress or change without warning or symptoms, it is very important to have your eyes checked as often as your eye doctor recommends. Keeping eye pressure under control can slow or stop damage to the optic nerve and continued loss of vision. Early detection, prompt treatment, and regular monitoring can help to control glaucoma and reduce the chances for vision loss.